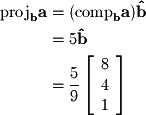The orthogonal projection of a vector  onto another vector
onto another vector 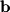 is a vector that has a magnitude equal to
is a vector that has a magnitude equal to 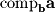 and direction equal to the direction of
and direction equal to the direction of 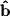 . Another way to think of an orthogonal projection is that it is the vector that would represent the "shadow" that
. Another way to think of an orthogonal projection is that it is the vector that would represent the "shadow" that  casts onto
casts onto 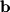 if a light were held directly above and at a
if a light were held directly above and at a 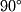 degree angle to
degree angle to 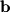 .
.
We already know how to find the magnitude of this vector by finding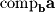 so we simply need to rescale
so we simply need to rescale 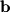 by this magnitude. Thus, we normalize
by this magnitude. Thus, we normalize 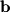 and multiply by
and multiply by 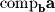 :
: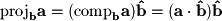
 onto another vector
onto another vector 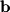 is a vector that has a magnitude equal to
is a vector that has a magnitude equal to 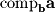 and direction equal to the direction of
and direction equal to the direction of 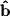 . Another way to think of an orthogonal projection is that it is the vector that would represent the "shadow" that
. Another way to think of an orthogonal projection is that it is the vector that would represent the "shadow" that  casts onto
casts onto 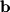 if a light were held directly above and at a
if a light were held directly above and at a 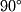 degree angle to
degree angle to 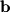 .
.We already know how to find the magnitude of this vector by finding
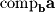 so we simply need to rescale
so we simply need to rescale 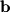 by this magnitude. Thus, we normalize
by this magnitude. Thus, we normalize 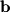 and multiply by
and multiply by 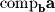 :
: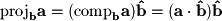
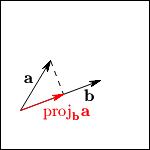
Figure 2-10.
Orthogonal Projection of  onto
onto 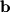
 onto
onto 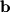
Excercise 2-7.
Find the component of vector  along the direction of vector
along the direction of vector 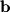 . After finding this component, find the orthogonal projection of
. After finding this component, find the orthogonal projection of  onto
onto 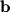 .
. 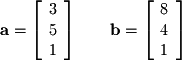
 along the direction of vector
along the direction of vector 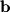 . After finding this component, find the orthogonal projection of
. After finding this component, find the orthogonal projection of  onto
onto 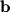 .
. 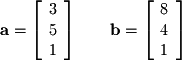
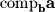 can be found by applying the definition of vector components:
can be found by applying the definition of vector components: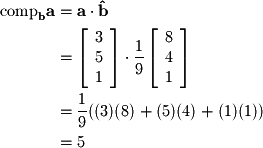
 that lies along the direction of
that lies along the direction of 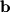 . In order to find the orthogonal projection we simply need to multiply the unit vector
. In order to find the orthogonal projection we simply need to multiply the unit vector 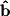 by 5:
by 5: